If you use a computer every day, you rely on the motherboard more than you realize. While the CPU is the “brain” of the system, the motherboard is the backbone that connects and powers every major component — from your processor and RAM to your SSD, GPU, and cooling system.
Whether you’re building a PC, upgrading hardware, or troubleshooting performance issues, understanding how a motherboard works is essential.
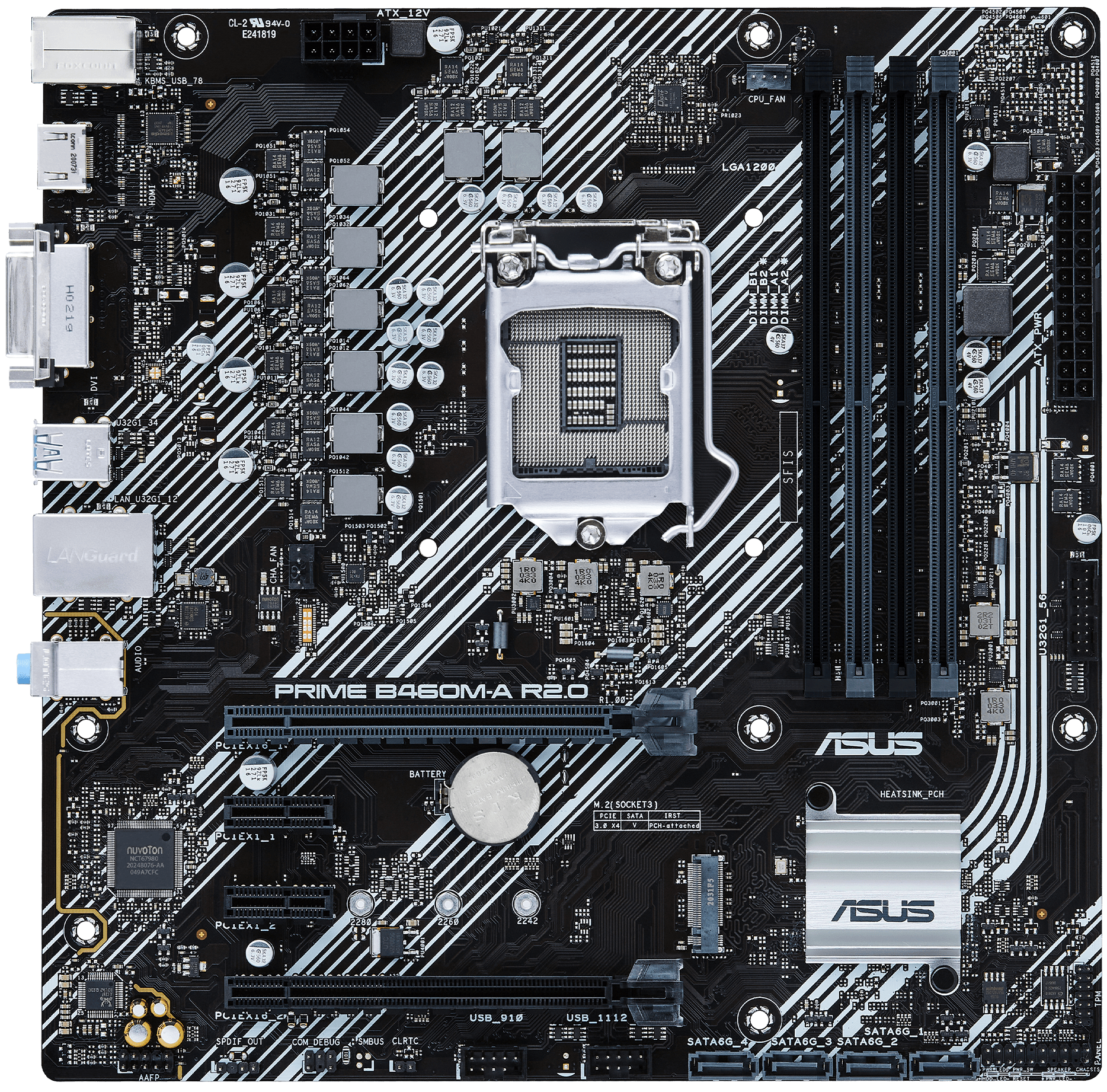
A motherboard (also known as the mainboard or system board) is the primary circuit board inside your computer. It provides:
- Physical connection for all components
- Power distribution
- Communication pathways (buses and lanes)
- Support for the CPU, RAM, storage, and I/O ports
Without a motherboard, a computer cannot function — all hardware components rely on it to send signals, receive instructions, and communicate with Windows.
How a Motherboard Works
A motherboard acts as a central hub that allows data to travel between components using:
1. Chipset
The chipset is the motherboard’s “traffic controller,” determining:
- Which CPUs are supported
- How many USB ports you can use
- PCIe lane availability
- Memory compatibility
- Overclocking support
Modern chipsets (Intel Z790, AMD X670E, B550, etc.) define the capabilities of your entire PC.
2. BIOS/UEFI Firmware
This is the firmware stored on the motherboard that:
- Initializes your hardware
- Boots Windows
- Allows settings changes (boot order, CPU settings, RAM timings)
Modern boards use UEFI, a faster and more secure BIOS replacement.
3. Power Delivery System (VRM)
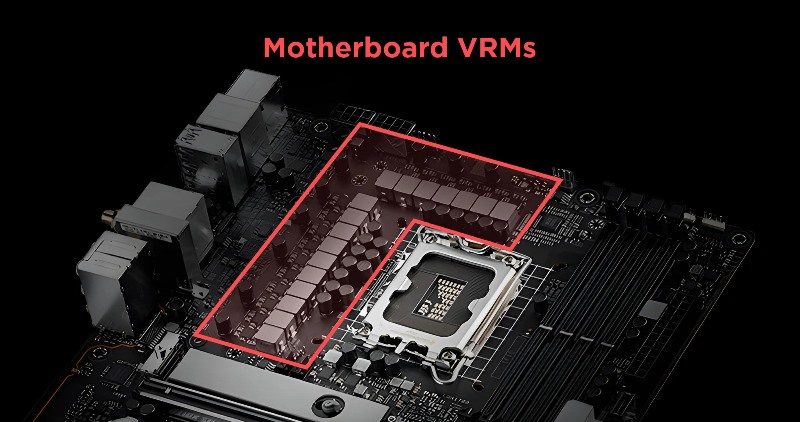

Voltage Regulator Modules (VRMs) ensure stable power for the CPU.
Better VRMs = higher performance and better overclocking stability.
Key Parts of a Motherboard
1. CPU Socket
The physical slot for the processor. Compatibility depends on:
- Socket type (LGA1700, AM5, AM4, etc.)
- Chipset support
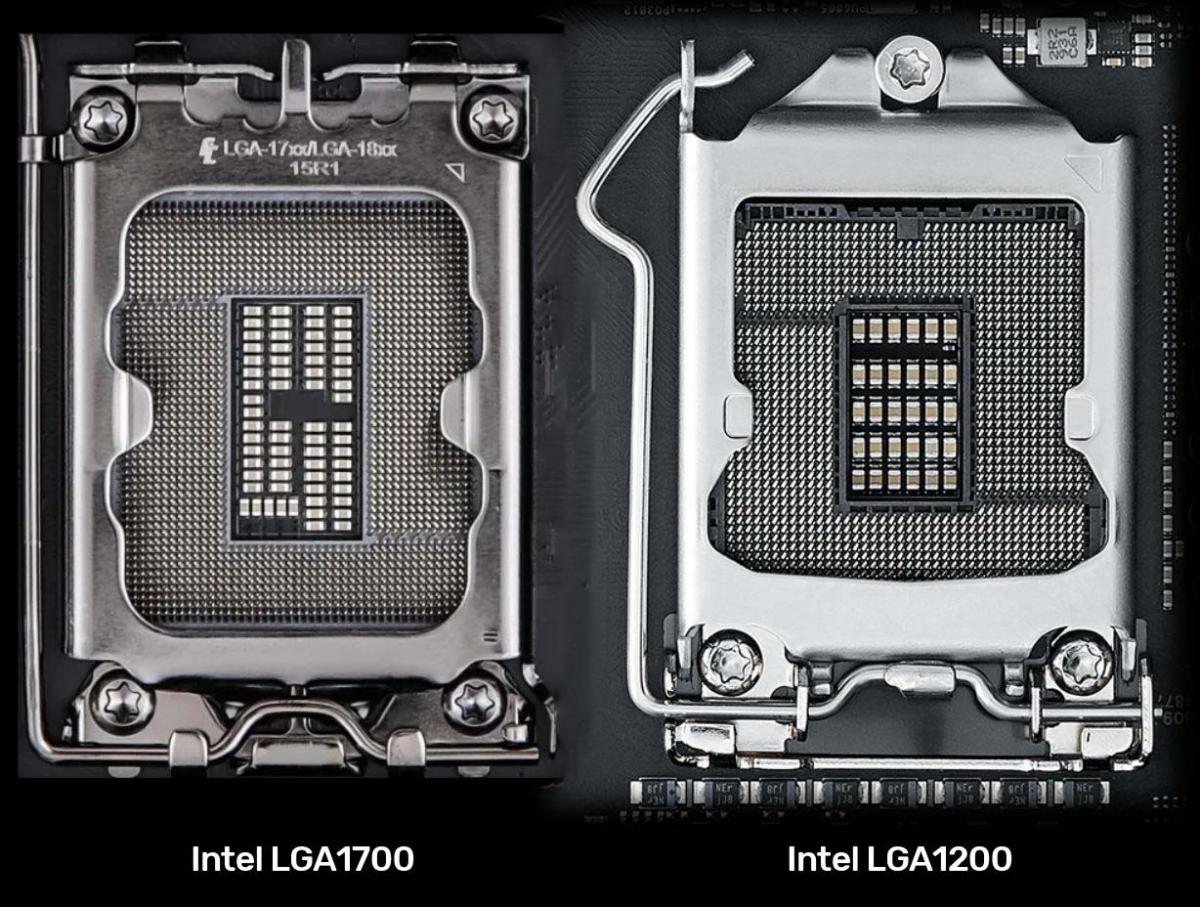

If the socket doesn’t match, the CPU won’t fit — even if it’s the same brand.
2. RAM Slots (DIMM Slots)
Where your memory sticks install.
- DDR4 vs. DDR5
- Maximum RAM speed
- Dual-channel / quad-channel support
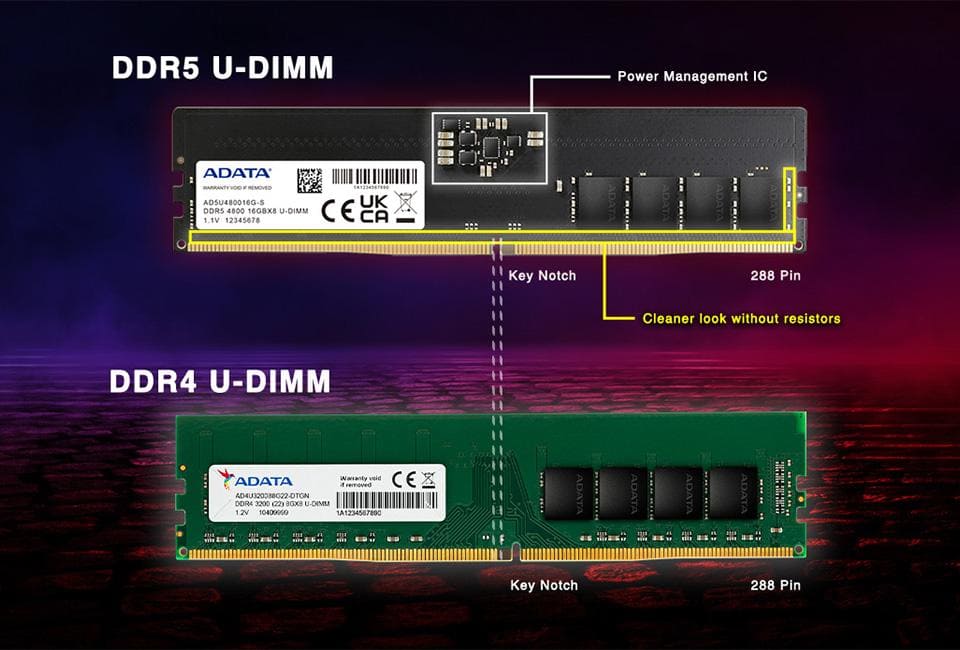
More RAM slots usually mean more expandability.
3. PCIe Slots
These slots connect graphics cards, Wi-Fi cards, capture cards, and more.
PCIe generations:
- PCIe 3.0 – older standard
- PCIe 4.0 – common today
- PCIe 5.0 – fastest, used in next-gen GPUs and SSDs
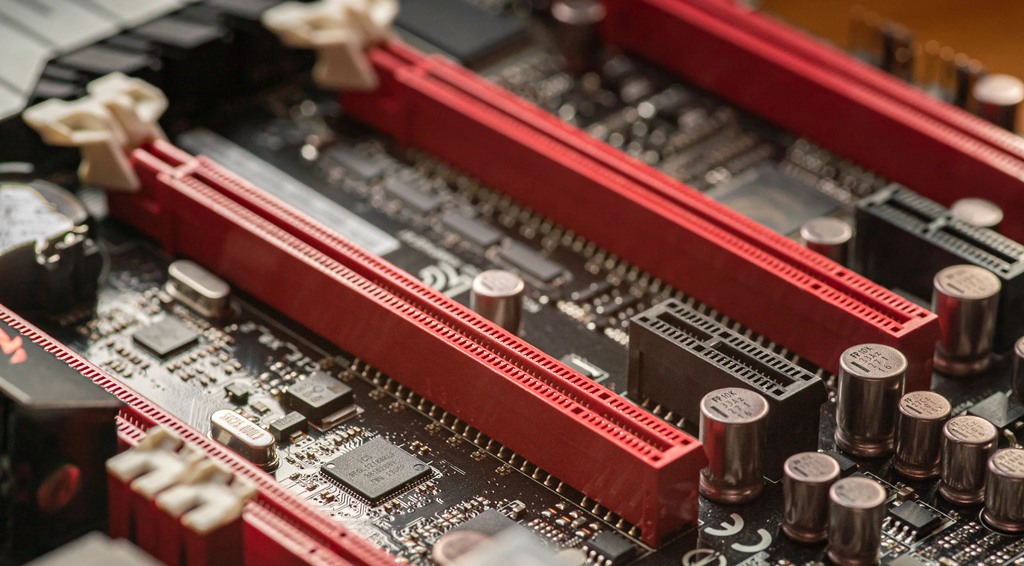
4. M.2 Slots for SSDs
Modern motherboards have multiple M.2 slots supporting:
- NVMe SSDs (very fast)
- SATA M.2 SSDs (slower)
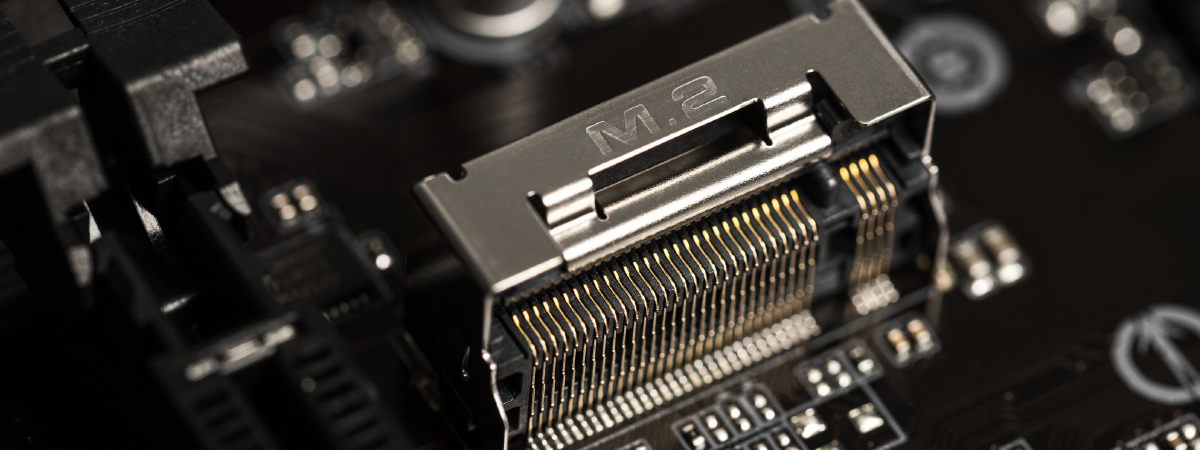
Some boards support PCIe 5.0 SSDs, offering extreme speed.
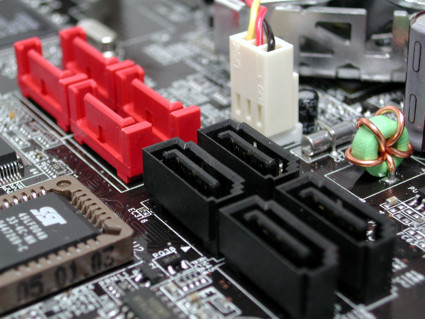
5. SATA Ports
Used for older storage:
- 2.5” SSDs
- HDDs
- Optical drives
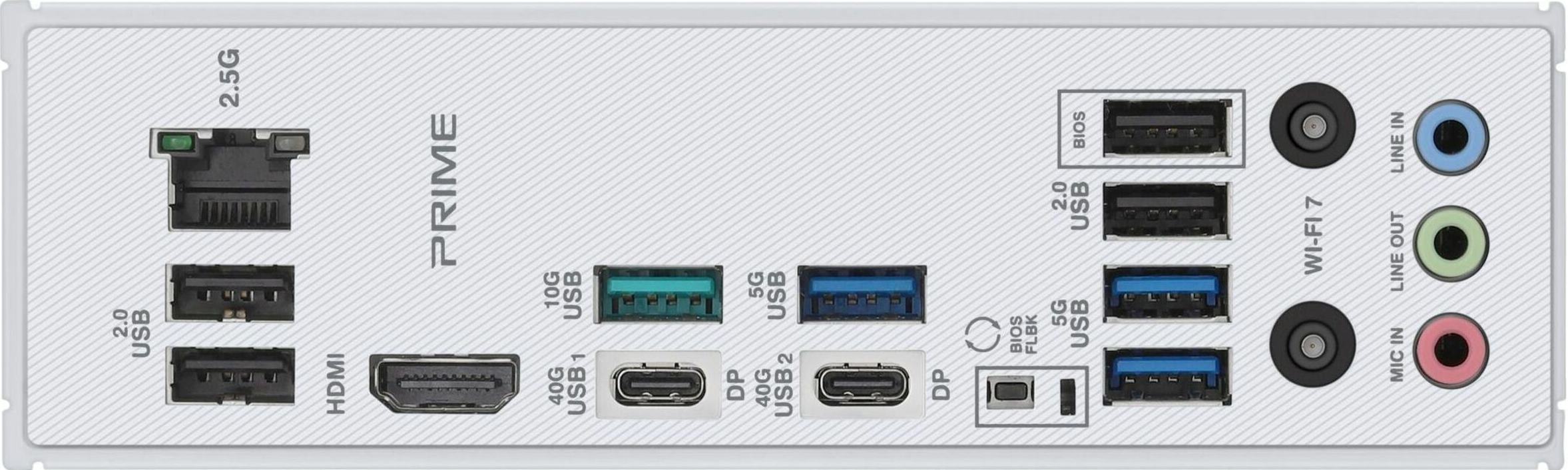
6. Rear I/O Ports
Typical ports include:
- USB-A / USB-C
- HDMI / DisplayPort (if iGPU available)
- Ethernet (1Gbps, 2.5Gbps, 10Gbps)
- Audio jacks
- Wi-Fi antenna connectors
7. Internal Connectors
Inside the case, the motherboard includes:
- Front panel connectors
- CPU fan and pump headers
- RGB/ARGB headers
- USB headers
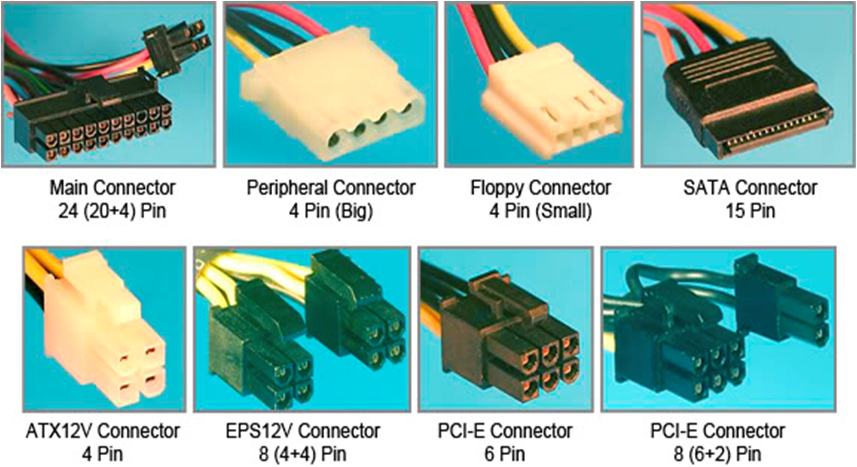
- 24-pin power connector
- 8-pin CPU power connector
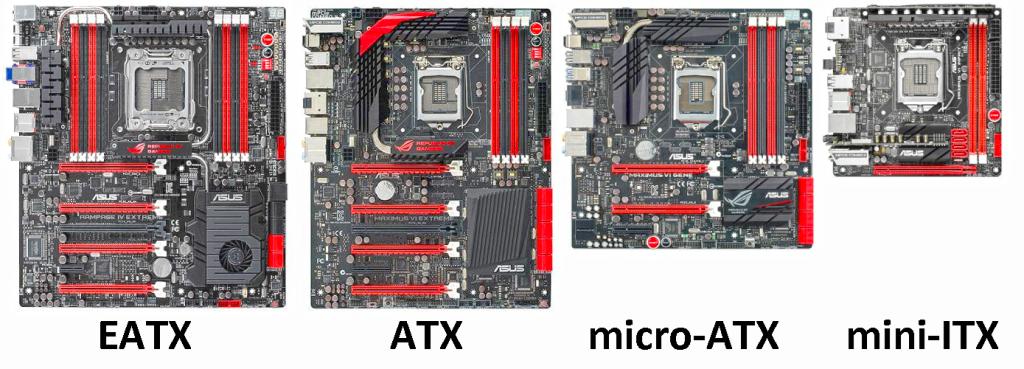
Types of Motherboards
Motherboards come in different form factors depending on the size of your PC case.
1. ATX (Standard)
- Most common
- Best for gaming and productivity
- Many ports and expansion slots
2. Micro-ATX
- Smaller, cheaper
- Fewer PCIe slots
- Great for budget builds
3. Mini-ITX
- Very small
- Perfect for compact PCs
- Limited expandability
4. E-ATX
- Oversized
- High-end enthusiast builds
- Best VRMs and cooling
How the Motherboard Affects PC Performance
While the motherboard doesn’t directly increase FPS, it impacts performance by:
✔ Supporting faster CPUs
✔ Allowing faster RAM speeds
✔ Enabling PCIe 4.0/5.0 for GPUs and SSDs
✔ Providing higher-quality VRMs
✔ Offering better thermals
✔ Improving system stability under heavy loads
A cheap or outdated motherboard can bottleneck high-end hardware.
Common Motherboard Features to Look For
When choosing a motherboard for Windows PCs, consider:
✔ Socket compatibility
Make sure it supports your CPU (Intel LGA1700, AMD AM5, etc.)
✔ Chipset
Higher-end chipsets support:
- More USB ports
- More PCIe lanes
- Overclocking
- Better BIOS features
✔ RAM support
DDR4 vs. DDR5, max frequency, and number of slots.
✔ M.2 slots
More M.2 slots = better storage flexibility.
✔ USB ports
Look for USB-C and high-speed USB 3.2 Gen 2.
✔ VRM quality
Important for gaming and high-performance systems.
✔ Wi-Fi & Bluetooth
Wi-Fi 6 / Wi-Fi 6E recommended.
Signs Your Motherboard Might Be Failing
- PC won’t boot
- USB ports stop working randomly
- System freezes or restarts
- Burning smell or visible damage
- RAM/GPU not detected
- BIOS errors
If these issues appear, the motherboard may need repair or replacement.
How to Choose the Right Motherboard
🖥 Everyday Windows Use
- B550 / B650 (AMD)
- B660 / B760 (Intel)
- Micro-ATX is enough
🎮 Gaming
- AMD: B650 or X670E
- Intel: B760 or Z790
- At least 2–3 M.2 slots
- Strong VRMs
🎬 Video Editing / Productivity
- X670E or Z790
- DDR5 RAM support
- PCIe 5.0 SSD support
💼 Budget Builds
- B450, B550, H610, B660
- DDR4 memory for lower cost
Frequently Asked Questions (Motherboard FAQ)
Do motherboards improve gaming performance?
Not directly — but they affect CPU performance, RAM speed, and GPU compatibility.
Can a motherboard slow down a PC?
Yes. Weak VRMs, limited PCIe lanes, or slow RAM support can bottleneck performance.
Is it worth upgrading just the motherboard?
Only if you plan to switch to a newer CPU generation.
Can any motherboard support Windows 11?
Most modern boards do, but they must support TPM 2.0.
Conclusion
A motherboard is the foundation of every Windows PC. It connects all the hardware, manages communication between components, and determines what upgrades your system can support. Whether you’re gaming, editing videos, or building a new PC, choosing the right motherboard ensures better stability, speed, and long-term performance.

