If you use a computer, you rely on the CPU every single second — even if you’ve never thought about it. The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is often described as the brain of a computer because it carries out nearly every instruction required to run Windows, open apps, browse the web, and play games. Without it, the entire system would remain completely inactive.
A CPU (Central Processing Unit) is a small chip located on the motherboard that processes all the essential instructions your computer receives. Whenever Windows performs a task — from loading a file to running an app — the CPU interprets and executes the commands.
In simpler terms, the CPU decides what needs to be done, when it should happen, and how it’s carried out.
Modern processors from Intel and AMD contain billions of microscopic transistors. These transistors switch on and off to perform calculations at incredible speeds, measured in gigahertz (GHz).

How a CPU Works
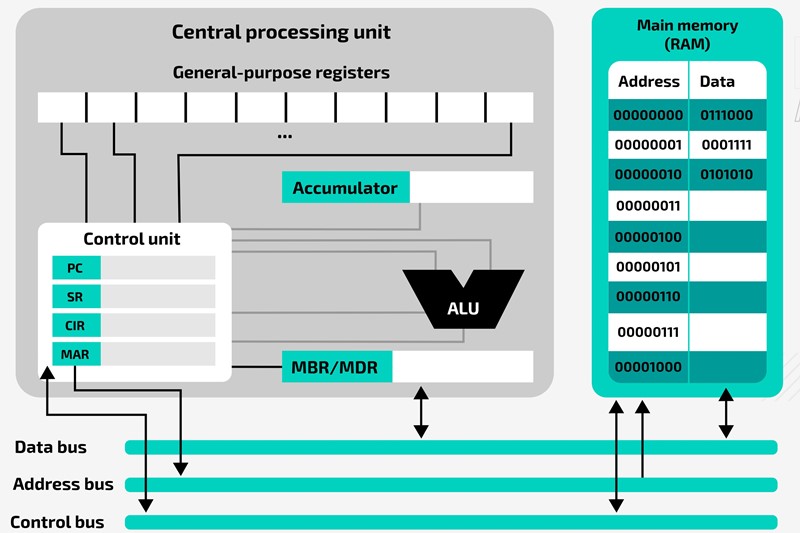
Every CPU works through three foundational steps:
1. Fetch
The processor retrieves instructions from system memory (RAM).
2. Decode
It translates the instructions into commands the CPU can understand.
3. Execute
The CPU performs the operation — such as rendering graphics, processing user input, or running app code.
This cycle repeats millions (or even billions) of times per second.
Picture : adacomputerscience.org
Cores and Threads: Why They Matter
Older CPUs had only one core, meaning they could handle one instruction at a time. Today’s CPUs have multiple cores, allowing them to perform several tasks simultaneously.
-
Cores: Separate processing units inside the CPU
-
Threads: Virtual processes that help the CPU multitask more efficiently
More cores and threads generally mean better performance in multitasking, video editing, gaming, and heavy workloads.
Picture : freepik.com
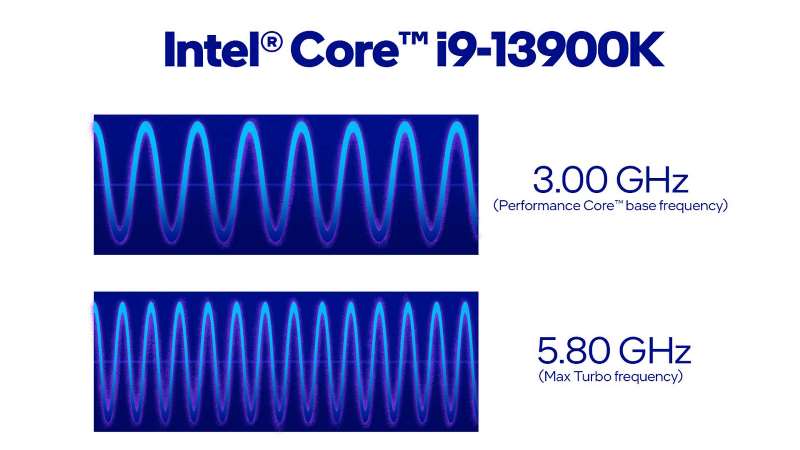
Clock Speed (GHz) Explained
Clock speed indicates how many cycles per second a CPU can perform. A processor running at 3.5 GHz can handle 3.5 billion cycles per second.
Higher clock speed = faster single-task performance.
However, core count is equally important for modern applications.
Picture : intel.com
Integrated Graphics vs. Discrete GPUs
Some CPUs include integrated graphics (iGPU), allowing a PC to display images without a dedicated graphics card.
-
CPUs with iGPU: Great for general users, browsing, office work
-
CPUs without iGPU: Require a separate GPU but usually offer higher performance overall
For gaming or professional creative work, a discrete GPU is recommended.

Picture : techguided.com
How the CPU Affects PC Performance
The CPU plays a key role in:
-
System responsiveness
-
App loading times
-
Gaming performance (especially in CPU-heavy titles)
-
Video editing and rendering
-
Software development and virtualization
A weak CPU can slow down a system even if you have fast RAM or an SSD.
Picture : educatecomputer.com
Choosing the Right CPU for Windows PCs
When buying or upgrading a processor, consider:
1. Intel vs. AMD
Both companies offer excellent processors for different budgets:
-
Intel Core i3/i5/i7/i9
-
AMD Ryzen 3/5/7/9
2. Number of Cores
-
4–6 cores: Everyday use, Windows tasks, light gaming
-
8–12 cores: Gaming, multitasking, content creation
-
16+ cores: Advanced workloads like 3D rendering or heavy editing
3. Clock Speed
Higher is better, especially for gaming and single-threaded tasks.
4. Compatibility
Ensure your motherboard socket supports your chosen CPU.

Signs Your CPU Might Be the Problem
If you’re experiencing:
-
High CPU usage in Task Manager
-
Slow Windows startup
-
Apps freezing or lagging
-
Poor gaming performance
-
Overheating during normal tasks
your processor may be outdated, overheating, or bottlenecked by other hardware.
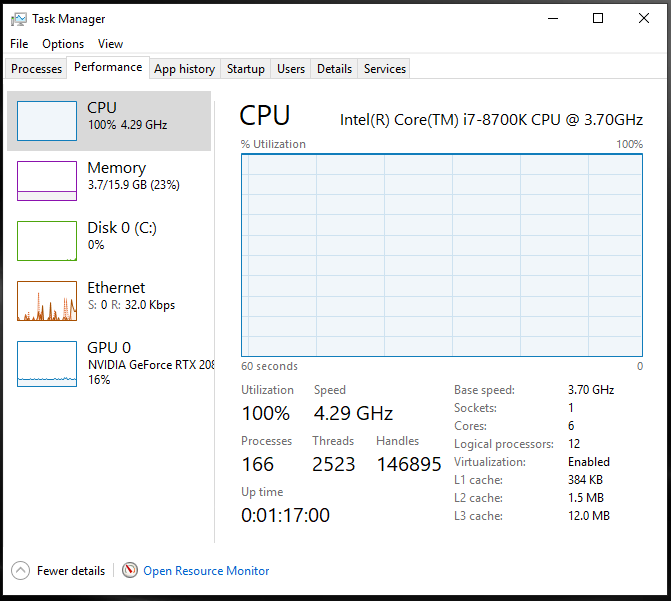
Picture : learn.microsoft.com
Conclusion: Why the CPU Matters
The CPU is the central component that determines how fast and efficiently your Windows PC runs. Understanding how it works can help you choose better hardware, optimize performance, and troubleshoot issues more effectively.
Whether you’re building a gaming PC or using a laptop for everyday work, choosing the right CPU will have the biggest impact on your overall experience.