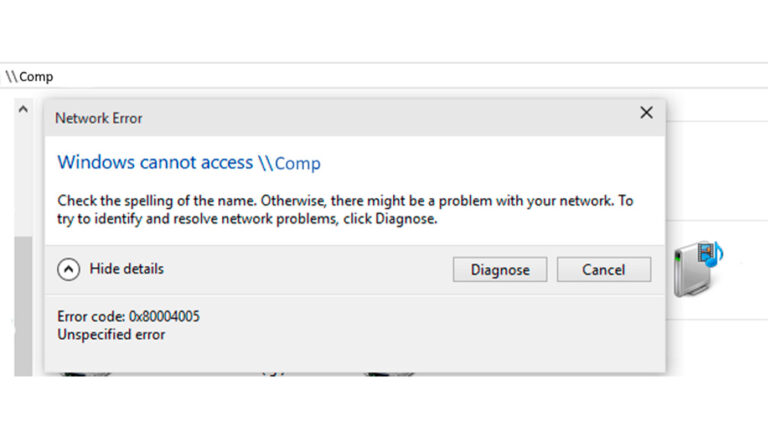
Overview of Error 0x80004005

In Windows 11 and Windows 10, you might see the message:
“Windows cannot access [resource]” — Error code 0x80004005 (Unspecified error)
This often happens when trying to connect to network shares, NAS storage, or another PC’s shared folders. Starting with Windows 10 version 1709 and Windows Server 2019, SMB2 and SMB3 clients block guest account connections by default, which can trigger this error.
Main Causes
-
Disabled insecure guest logins
-
SMB service not running or misconfigured
-
IPv6 or SMB version issues
-
Misconfigured local security policies
-
NTLM traffic restrictions in the registry
Step-by-Step Fixes
1. Enable Guest Access in Local Group Policy
-
Press Win + R, type
gpedit.msc, and press Enter. -
Go to:
-
Enable insecure guest logons.
-
Also, go to:
Find Microsoft network client: Digitally sign communications (always) and set it to Disabled.
-
Restart your PC.
2. Ensure SMB Services Are Running
-
Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
-
Check startup type:
-
If not set to
AUTO_START, run: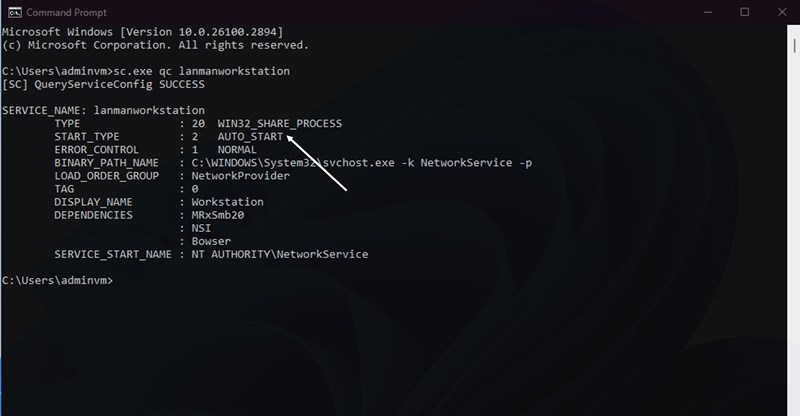
3. Allow Insecure Guest Authentication via Registry
Run these commands in Command Prompt (Admin):
4. Adjust Local Security Policy on Target PC
-
Press Win + R, type
secpol.msc. -
Go to:
-
Open Deny access to this computer from the network and remove “Guest”.
-
Turn off password-protected sharing in Network and Sharing Center.
Additional Solutions
-
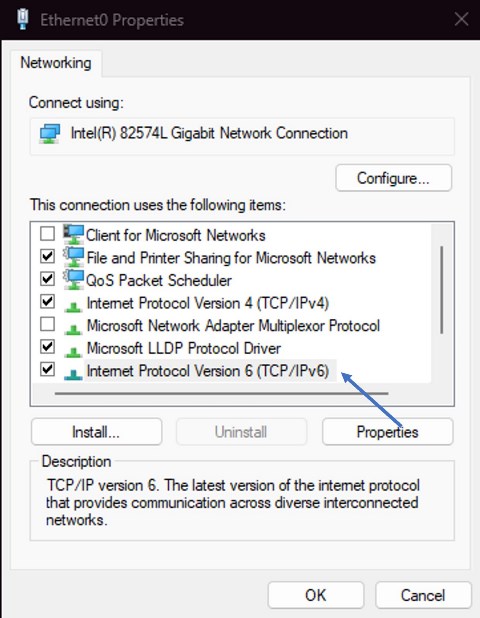
Disable IPv6:
Win + R → ncpa.cpl → Connection Properties → Uncheck IPv6. -
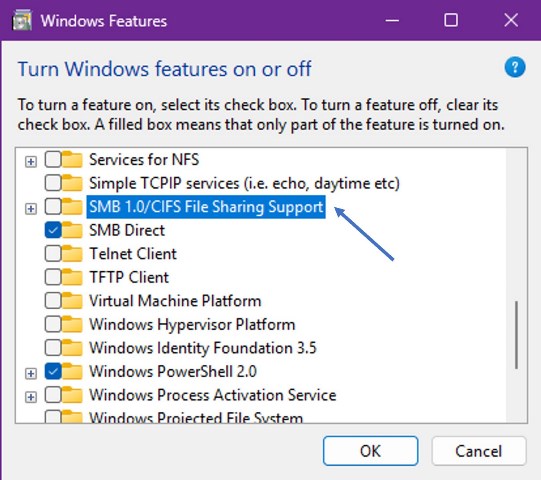
Enable SMB 1.0 if the device only supports older protocol.
-
Ensure services like Function Discovery Resource Publication, SSDP Discovery, and DNS Client are running.
-
Add saved credentials in Control Panel → Credential Manager → Windows Credentials.
-
Remove
RestrictReceivingNTLMTrafficorRestrictSendingNTLMTrafficin registry if present. -
Test disabling antivirus/firewall temporarily.
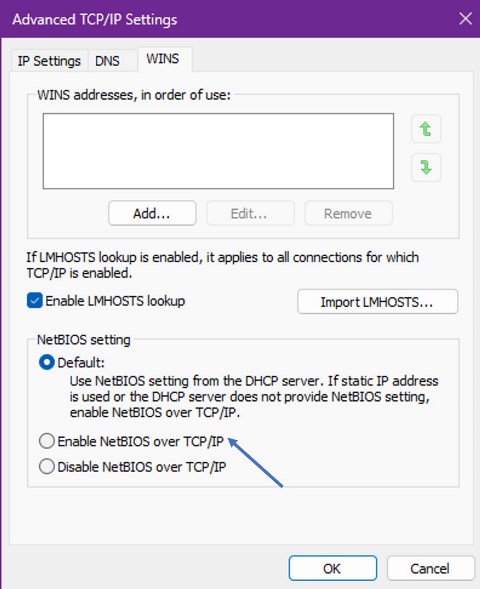
-
Enable NetBIOS over TCP/IP in IPv4 Advanced Settings.
-
Assign a static IP instead of DHCP.
✅ With these methods, most users can fix network error 0x80004005 in Windows 10/11 and restore access to shared folders or network drives.
Explore other helpful tools in our Windows utilities section.