The “Attempted Write to Readonly Memory” Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) appears when Windows detects that a driver or system process is trying to write data into a protected memory region. This memory is “read-only,” meaning no application has permission to modify it.
When a driver attempts to change this protected area, Windows instantly stops all processes and shows the 0x000000BE error to prevent data corruption.
This issue is common on Windows 10 and Windows 11 and often points to:
-
corrupt or outdated drivers
-
faulty RAM
-
conflicts with recently installed hardware
-
malware or system file corruption
The good news: this error is fixable in most cases.
Main Causes of “Attempted Write to Readonly Memory”
The error is almost always related to drivers or memory:
1. Faulty or incompatible drivers
Graphics drivers (NVIDIA, AMD, Intel) and network drivers are the most common triggers.
2. RAM issues or memory corruption
Defective memory modules cause Windows to fail when writing data.
3. Corrupted system files
Damaged Windows components lead to memory access conflicts.
4. Overclocking
CPU, GPU, or RAM overclock settings may cause instability.
5. Malware or unwanted software
Malicious apps can attempt to write into protected memory areas.
How to Fix “Attempted Write to Readonly Memory” (0x000000BE)
Below are the most effective solutions for Windows 10/11.
1. Update or Roll Back Problematic Drivers
Faulty drivers are the #1 reason for this BSOD.
Update drivers:
-
Press Win + X → Device Manager
-
Expand Display adapters, Network adapters, and System devices
-
Right-click → Update driver
Better option:
Download the latest drivers from manufacturer websites:
-
NVIDIA.com
-
AMD.com
-
Intel.com
-
Dell/HP/Lenovo support pages
Roll back drivers (if error started recently):
-
Device Manager
-
Select the device → Properties
-
Tab Driver
-
Click Roll Back Driver
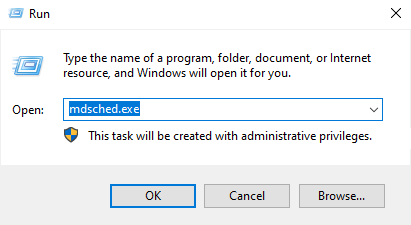
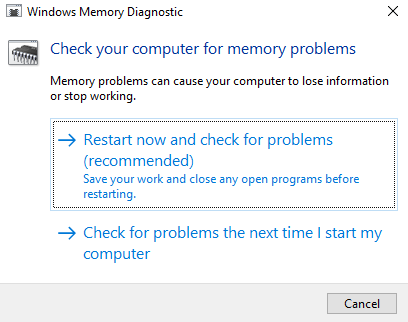
2. Run Windows Memory Diagnostic (check RAM) or Memtest86+
-
Press Win + R
-
Type:
- Select Restart now and check for problems
If Windows reports errors — one of your RAM sticks is bad.
Remove one module at a time and test again.
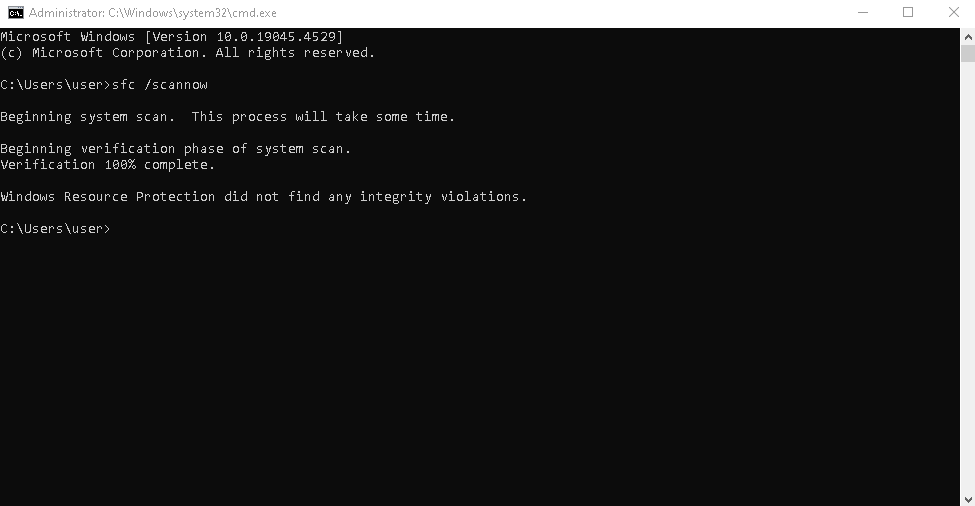
3. Run System File Checker (SFC) and DISM
Corrupt system files can easily trigger this BSOD.
Run these commands in Command Prompt (Admin):
Then run:
Restart your PC when finished.
4. Disable Overclocking
If you overclocked:
-
CPU
-
GPU
-
RAM (XMP/DOCP profiles)
Return everything to default through BIOS or software like MSI Afterburner.
Overclocking often creates unstable memory access → BSOD.
5. Scan Your PC for Malware
Use Windows Defender or any trusted antivirus.
Run a full system scan:
-
Windows Security
-
Virus & threat protection
-
Scan options → Full scan
Malware sometimes injects code into protected memory → causing the error.
6. Check Recently Installed Software / Drivers
If the BSOD appeared after installing:
-
a printer driver
-
a system utility
-
a game
-
new hardware
— uninstall it and restart.
Control Panel → Programs and Features → Uninstall suspicious apps.
7. Reset Windows Memory Caches via Command Prompt
Advanced fix:
Run these commands one by one:
Then restart your PC.
8. Perform a Clean Boot
This helps identify whether a startup app causes the crash.
-
Press Win + R → msconfig
-
Go to Services → check Hide all Microsoft services
-
Click Disable all
-
Restart your PC
If the BSOD disappears — one of the startup apps is responsible.
When You Should Replace RAM
Replace RAM if:
-
Windows Memory Diagnostic shows errors
-
The PC crashes randomly
-
BSODs appear even after a clean Windows install
RAM defects are extremely common with this BSOD.
FAQ
What causes “Attempted Write to Readonly Memory” (0x000000BE)?
This BSOD is caused by faulty drivers, RAM problems, corrupted system files, malware, or unstable overclock settings.
Is the error dangerous?
It can be. The BSOD protects your data, but repeated crashes indicate hardware or driver issues that must be fixed.
How do I know if RAM is faulty?
Run Windows Memory Diagnostic. If the test shows errors, one of your RAM sticks is damaged.
Can outdated GPU drivers cause this?
Yes. Graphics drivers are the most common cause of this BSOD, especially after Windows updates.
Will reinstalling Windows fix the issue?
A clean reinstall may help, but if the RAM or hardware is defective, the error will return.
Explore other helpful tools in our Windows utilities section.